
Salt production method
Outline of salt production
Since ancient times in Japan salt has been produced using a unique method: by making salt concentrate (about 20% salt) from seawater as the first step, then by boiling down the concentrate to crystallize the salt. This method is necessary because there are no salt lakes or rock salt in Japan and because salt production using natural solar evaporation is not suitable in the Japanese climate of heavy rainfall and high humidity.
Taking seawater
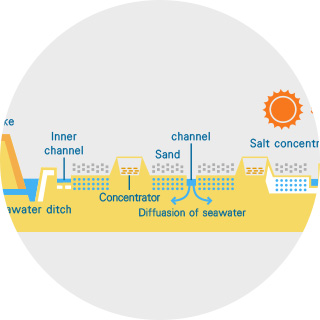
Salt concentrate production process
Concentration of seawater
- <Methods>
- using salt fields (banked salt-terrace, channeled salt-terrace and sloping salt-terrace) or ion-exchange membrane electrodialysis.
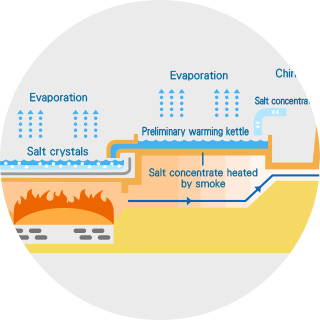
Boiling-down process
Boiling-down salt concentrate
- <Methods>
- using earthenware salt-boiling vessels or salt-kettles (clay, stone and iron kettles) or a vacuum evaporation system.
In addition to the above, salt is produced in Japan from imported sun-dried salt by dissolving and recrystallizing the salt or by grinding the salt.
Development of salt production technologies
Since ancient times in Japan salt has been produced using a unique method: by making salt concentrate (about 20% salt) from seawater as the first step, then by boiling down the concentrate to crystallize the salt. This method is necessary because there are no salt lakes or rock salt in Japan and because salt production using natural solar evaporation is not suitable in the Japanese climate of heavy rainfall and high humidity.
| Salt concentrate production process | Boiling-down process | |
|---|---|---|
| Ancient times | From earliest times salt was produced using seaweed. Later, salt concentrate was made using sand and the concentrate was then boiled down to produce salt. | Earthenware vessels and salt-kettles were developed for salt production. |
| Middle Ages | The construction of channels and ridges, etc. to produce salt concentrate began and salt beaches were developed at this time. There were two types of salt beaches: Irihama(channeled) and Agehama(banked). The two types differed in the means by which the brine was supplied. | Bamboo, clay, stone and iron salt-kettles were used. |
| 17th century | Channeled salt-terraces were developed, centering on the shores of the Setonaikai Sea, a region blessed with a good climate and topography, etc., and so salt production flourished here at this time. The use of the channeled salt-terrace system continued until modern times. | |
| Late 1920s-circa 1930 | Open iron kettles were replaced by salt-kettles with a steam heating system. Studies began into vacuum evaporation. | |
| Circa 1950 | Sloping salt-terraces were developed for salt concentrate production, replacing the channeled salt-terraces which had been in use for a long time. | The vacuum evaporation method became the usual method for boiling down. |
| Circa 1970 | The ion-exchange membrane electrodialysis method, which directly concentrates the salt in the seawater, was introduced and completely replaced the method of evaporating and removing water. | |
| 1997 | The Government Monopoly in Salt Act which had been in force for 92 years since 1905 was replaced by the Salt Business Law. The number of salt manufacturers is increasing and salt is now produced in various ways. | |
